Equilibrium-Driven Vertical Federated Learning with Selective Privacy Protection
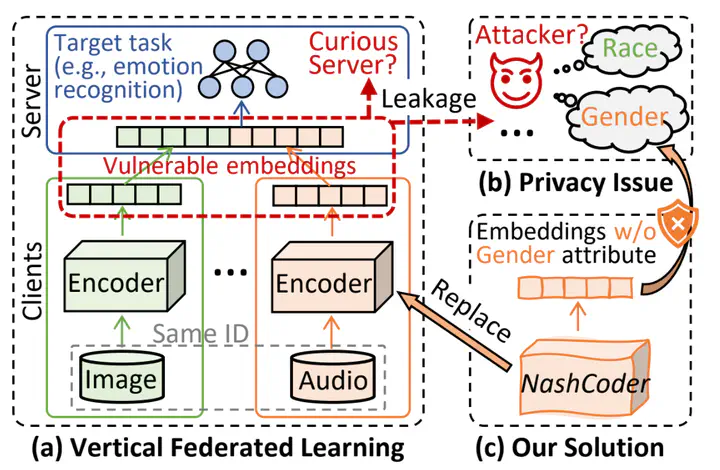 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) enables multiple clients with feature-partitioned data to collaboratively train models while preserving privacy by transmitting embeddings instead of raw data. However, such embeddings can still expose sensitive attributes (e.g., gender or race) unrelated to the target task, making them vulnerable to attribute inference attacks. Most existing privacy strategies may provide extra protection, but at the cost of reduced accuracy and excessive privacy budget. In this paper, we propose a novel equilibrium-driven VFL framework with selective privacy protection for sensitive attributes that are difficult to isolate from embeddings, thereby enhancing local privacy with minor accuracy compromise. We introduce two key innovations: (1) a NashCoder, which incorporates a surrogate head to jointly optimize accuracy and privacy; and (2) an adaptive decomposition strategy based on Shapley values, which dynamically decomposes the global objective for distributed optimization from an equilibrium perspective. We theoretically analyze our framework and empirically evaluate it on three public datasets against five baselines, demonstrating significant improvements in the accuracy-privacy trade-off under various privacy settings. Extensive experimental results support our theoretical analysis.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.