Abstract
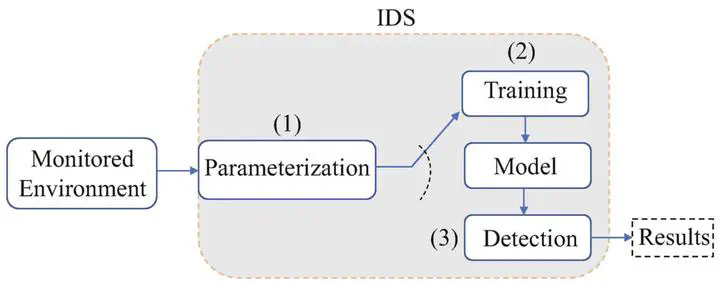
Recent works have revealed that network traffic packet detection systems (intrusion detection) are vulnerable to adversarial examples (AEs), where attackers can create AEs to make the detection system predict wrong network activities. Existing attacks only add a small perturbation to revise the network packets to obtain a high attack effectiveness. However, these AEs are crafted based on the white-box setting. It is unclear if such AEs can transfer to other black-box models, which could involve more security concerns. Therefore, in this chapter, we aim to explore the properties of the AEs’ transferability. To further understand the effectiveness of transfer attacks in the network domain, we first review the existing network intrusion detection systems and build different well-trained models (e.g., with different parameters and structures). Then, we employ various existing attack methods to generate different AEs based on specific surrogate models. To explore the transferability of AEs, we use different AEs to interact with different well-trained models, in order to find the key insights of transfer attacks in the network. We find that transfer attacks have some common properties with white-box attacks, and these findings may inspire more effective transfer attacks in future works.
#Create your slides in Markdown - click the Slides button to check out the #example.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.